NT-I7은 독보적인 T 세포 증폭제 입니다.
인터루킨-7 (Interleukin-7, IL-7)은 T 림프구 발달과 생존에 중심적인 역할을 합니다.
인터루킨-7은 CD4+ (조력 T세포)와 CD8+ (살상 T세포)에 작용하며, 나이브 T세포와 기억 T세포의 표면에 발현되는 인터루킨-7 수용체 (Interleukin-7 receptor, IL-7R)를 통해 T세포를 활성화 시킵니다. 따라서 인터루킨-7은 주요 T세포 세부종류들의 분화, 유지, 그리고 기능을 촉진 합니다. 반면에, 인터루킨-7 수용체는 조절 T세포에는 거의 발현되지 않는데, 이 T 세포종류는 T세포 반응을 제한 하는 역할을 합니다4.
네오이뮨텍은 IL-7을 기반으로 한 면역 기능향상을 위한 치료법을 연구중에 있습니다.

NT-I7은 인터루킨-7의 강화된 형태로 체내에서 더 안정적이며 T세포 증폭 효과가 오래 지속되게 합니다.
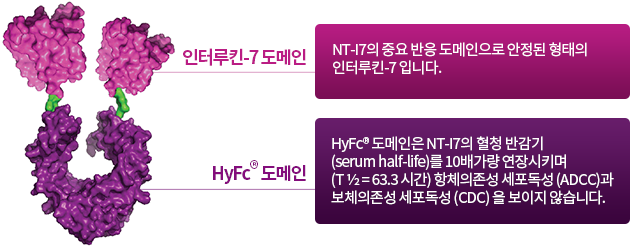
NT-I7은 환자들의 면역기능을 향상시킬 수 있도록 T세포의 양과 기능성을 강화하여 잠재적으로 더 큰 치료 혜택을 제공할 수 있습니다.
자세히 알아보기 NT-I7의 감염증 치료 기작에 관해
자세히 알아보기 NT-I7의 면역질환 치료 기작에 관해
자세히 알아보기 연구 포스터 및 논문 보기

1. Mazzucchelli, Renata, and Scott K. Durum. "Interleukin-7 receptor expression: intelligent design." Nature Reviews Immunology 7.2 (2007): 144-154.
2. Fry, Terry J., and Crystal L. Mackall. "Interleukin-7: from bench to clinic." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 99.11 (2002): 3892-3904.
3. Ponchel, Frederique, et al. "Interleukin-7 deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis: consequences for therapy-induced lymphopenia." Arthritis Res Ther 7.1 (2004): R80.
4. Seddiki, N. Santner-Nanan B, Martinson J, Zaunders J, Sasson S, Landay A, Solomon M, Selby W, Alexander SI, Nanan R, Kelleher A, Fazekas de St Groth B. "Expression of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 receptors discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells." J Exp Med 203 (2006): 1693-1700.
항상성 세포 증식
췌장암 환자에서는 3주차까지 ALC가 기준선에서 3배 이상 증가되었고, 이후 관찰 기간 동안에도 증가된 상태였습니다.
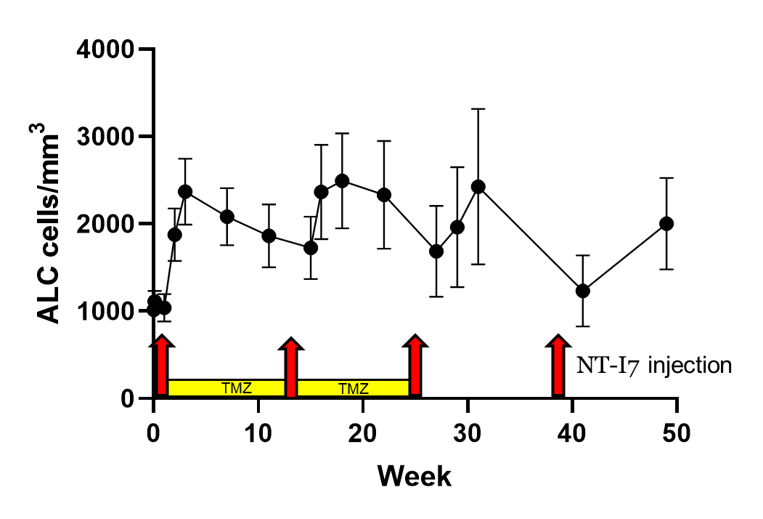
화학 치료로 인해서 면역 체계가 약해진 교모세포종 환자에서도 ALC가 상당히 증가되었습니다.
절대 림프구 수치 (ALC)
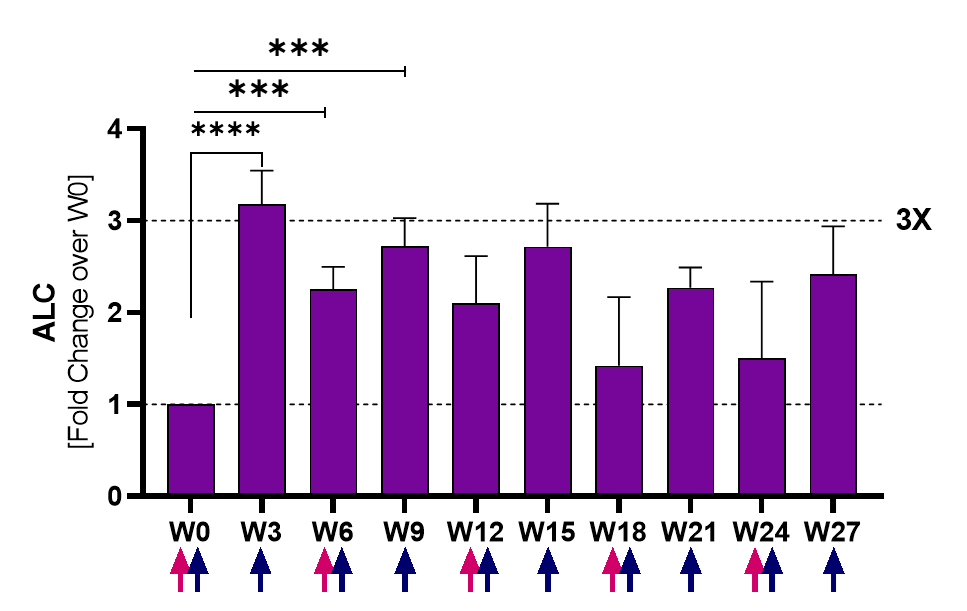
17명의 환자에서 림프구(ALC)가 3주차까지 기준선에서 3배 이상 증가되었고, 이후 관찰 기간 동안에도 증가되어 있는 것을 확인하였습니다.
화학 치료인 테모졸로마이드(Temozolomide, TMZ)를 받은 환자임에도 림프구(ALC)가 증가되었으며, 증가된 수치가 유지된 것을 확인하였습니다.

17명의 환자에서 림프구(ALC)가 3주차까지 기준선에서 3배 이상 증가되었고, 이후 관찰 기간 동안에도 증가되어 있는 것을 확인하였습니다.

화학 치료인 테모졸로마이드(Temozolomide, TMZ)를 받은 환자임에도 림프구(ALC)가 증가되었으며, 증가된 수치가 유지된 것을 확인하였습니다.
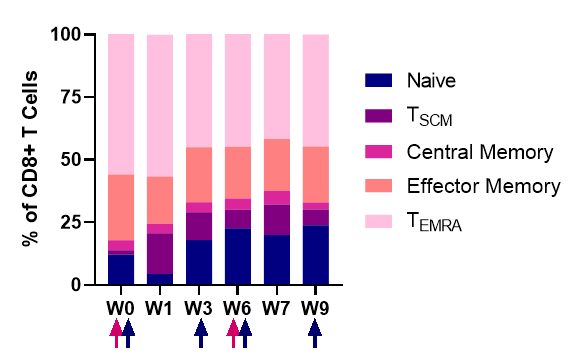
CD4+ 과 CD8+ T 세포
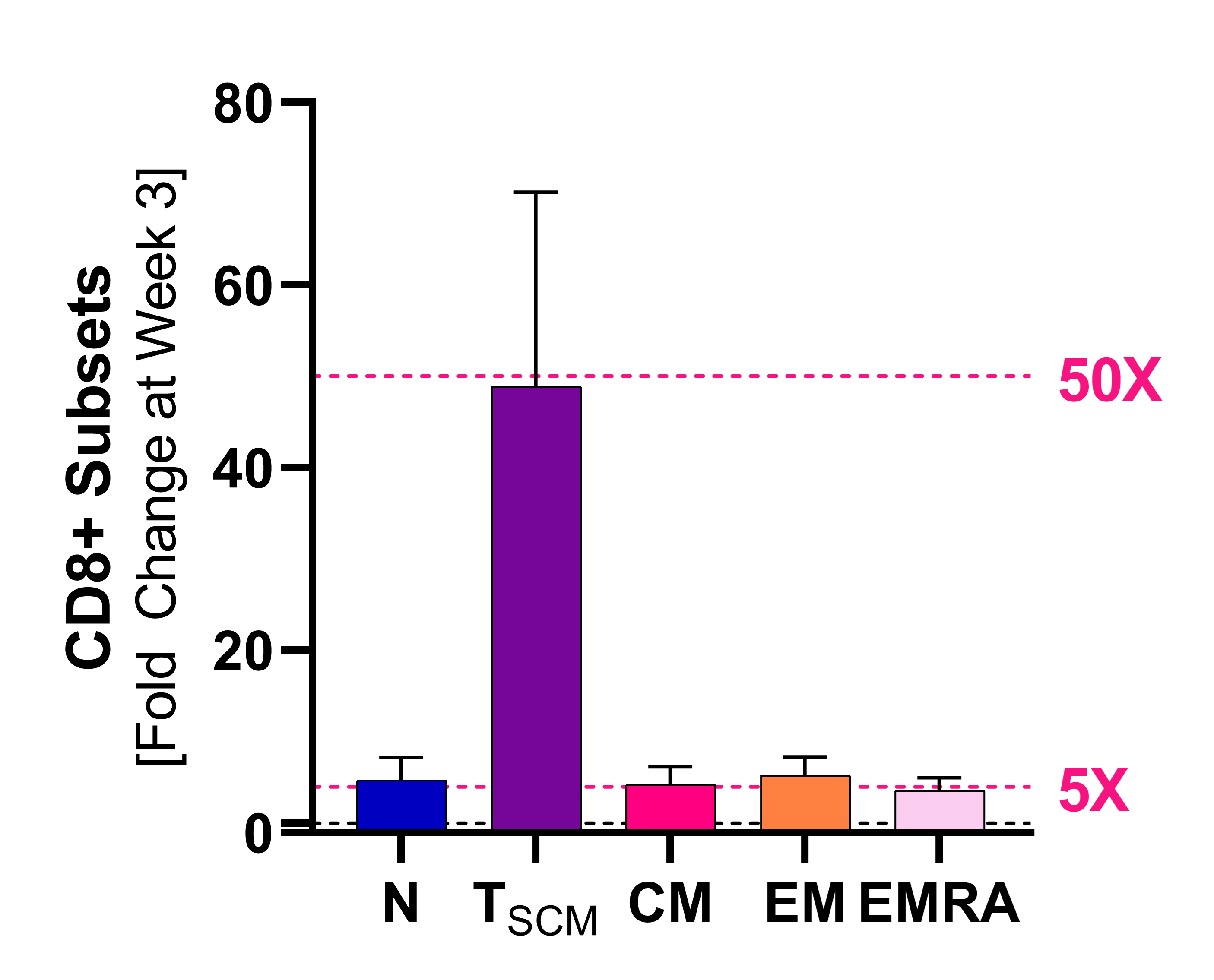
CD8+ T 세포 아형(subsets)
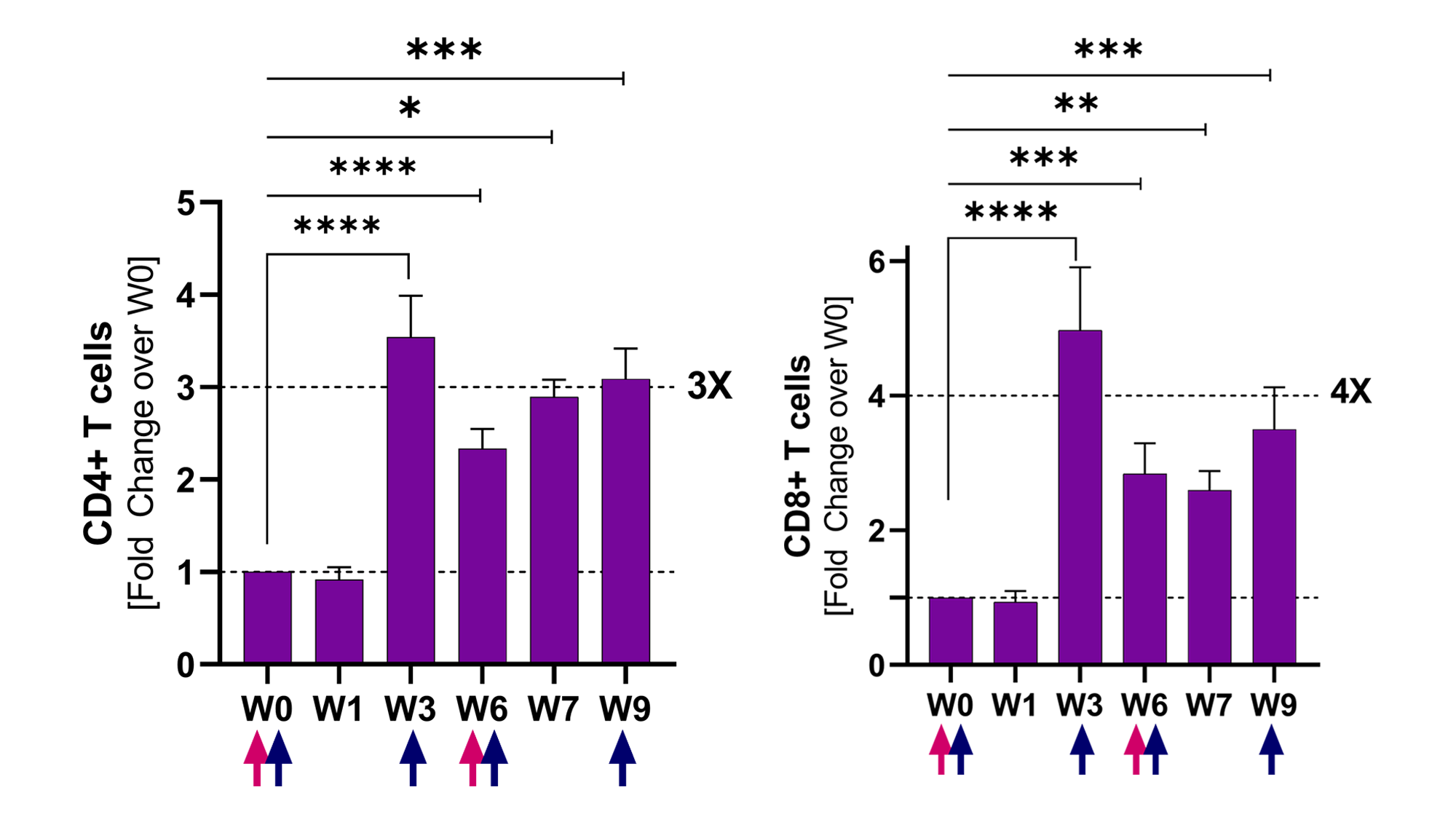
17명의 환자에서 CD4+와 CD8+ T 세포는 3주차까지 기준선에서 4배 이상 증가된 것을 확인하였으며, 9주차까지 증가된 T 세포가 유지된 것을 확인하였습니다.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
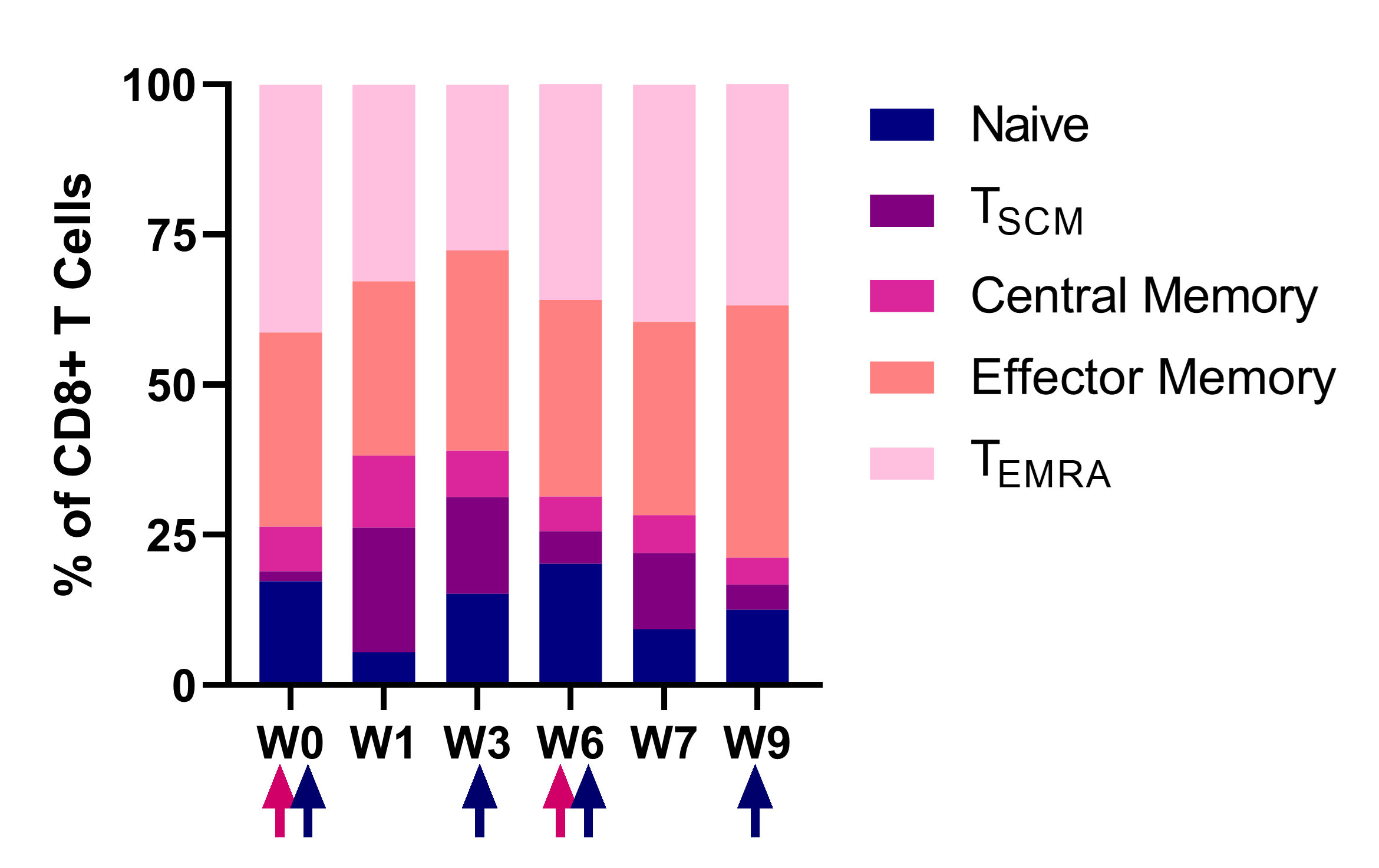
NT-I7의 투여 이후에 CD8+ T 세포의 종류는 다양해집니다. 세포 증식의 마커인 Ki67와 관련한 상향 조절은 재분배보다는 세포 증식이 T 세포의 증가를 주도하고 있음을 보여줍니다.

17명의 환자에서 CD4+와 CD8+ T 세포는 3주차까지 기준선에서 4배 이상 증가된 것을 확인하였으며, 9주차까지 증가된 T 세포가 유지된 것을 확인하였습니다.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
CD8+ T 세포 아형(subsets)
NT-I7의 투여 이후에 CD8+ T 세포의 종류는 다양해집니다. 세포 증식의 마커인 Ki67와 관련한 상향 조절은 재분배보다는 세포 증식이 T 세포의 증가를 주도하고 있음을 보여줍니다.
Source
Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” (2021) J Immunoth Cancer 9(Suppl 2):A1-A1054
Zhou A, Rettig M, Foltz Jennifer. “NT-I7,a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion of CD8 T cells and NK cells and immune activation in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiation” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
종양 내 림프구(Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes, TIL) 증가
혈장 내 케모카인
종양 내 림프구(TIL)
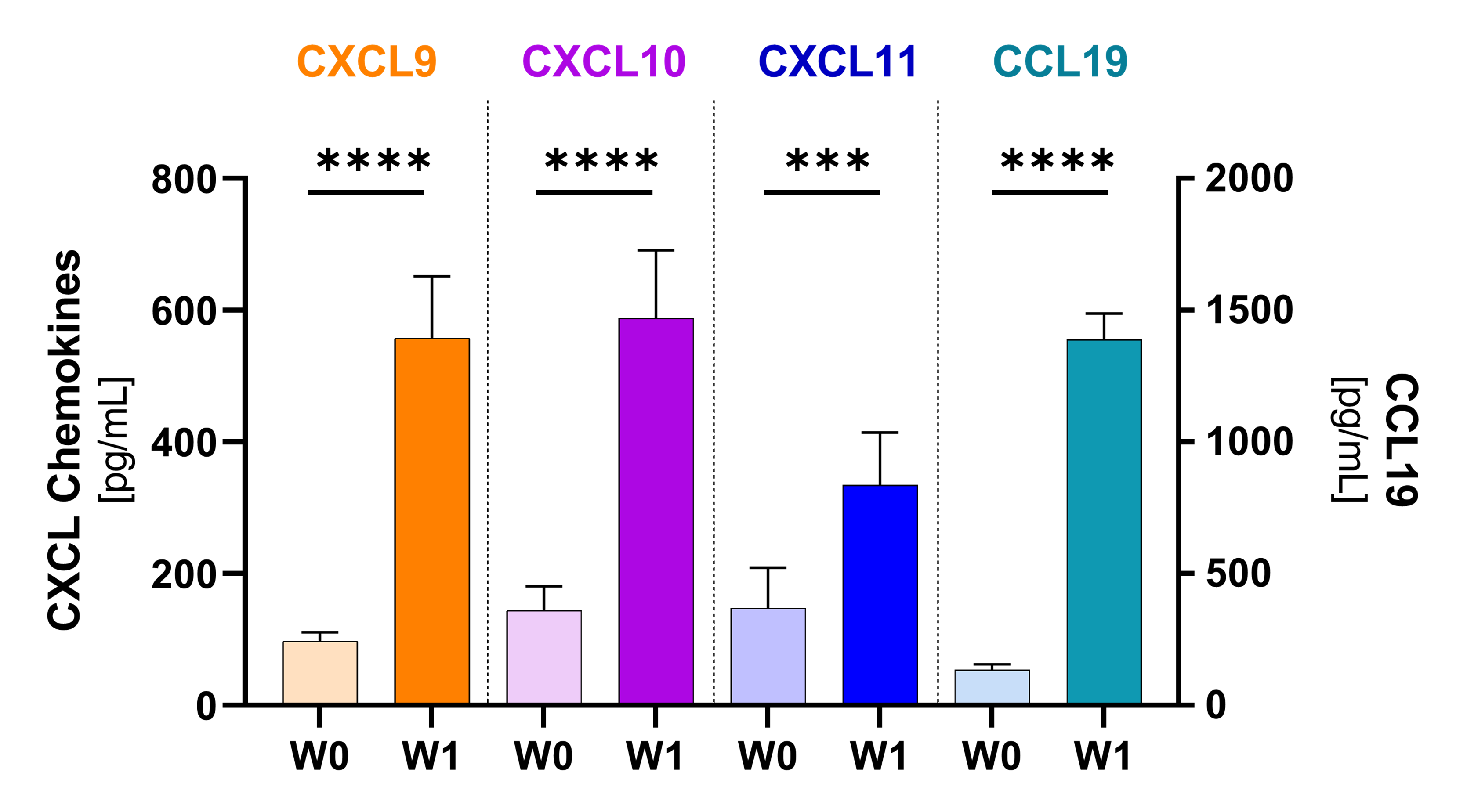
17명의 환자에서 강력한 화학 유인 물질 및 TLS 형성 매개체는 첫 번째 NT-I7+pembro 투여 후 크게 증가했습니다. 이 케모카인은 림프구를 종양으로 모집하고 T 세포의 항종양 활동을 촉진합니다.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
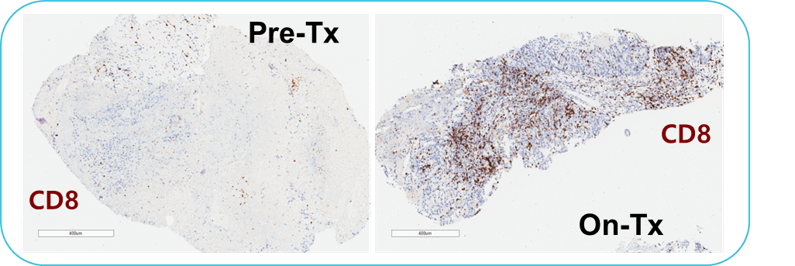
Pre-Tx = Pre-treatment & On-Tx = On-treatment.
투명 세포 난소암 환자의 대표적인 치료 전후 조직검사 결과 치료된 검체의 면역조직 화학적 염색 결과에서 CD8+ T 세포(갈색)의 상당한 증가를 보였습니다.
혈장 내 케모카인
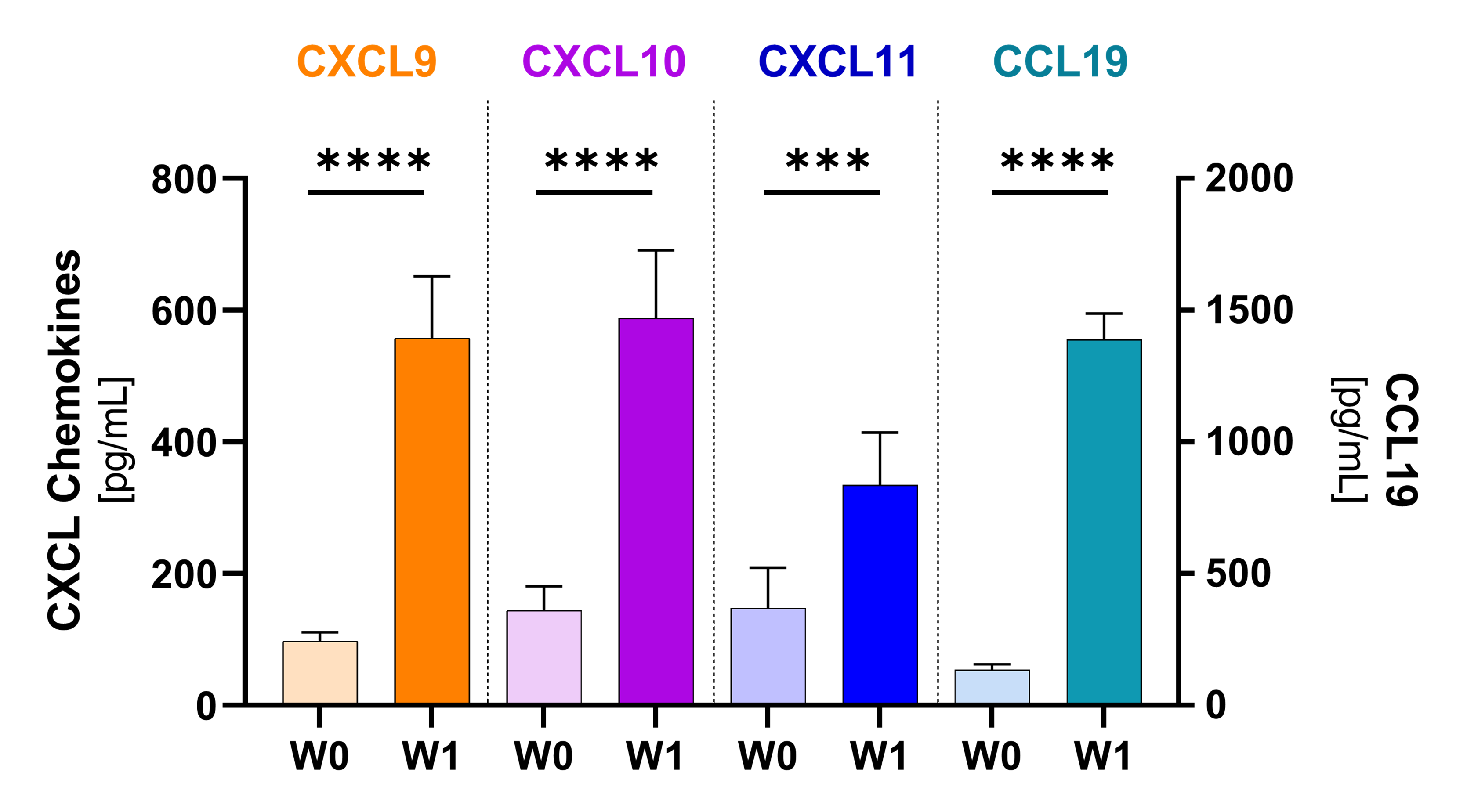
17명의 환자에서 강력한 화학 유인 물질 및 TLS 형성 매개체는 첫 번째 NT-I7+pembro 투여 후 크게 증가했습니다. 이 케모카인은 림프구를 종양으로 모집하고 T 세포의 항종양 활동을 촉진합니다.
(*p≤0.05; **p≤0.001; ***p≤0.0001; ***p≤0.00001)
종양 내 림프구(TIL)

Pre-Tx = Pre-treatment & On-Tx = On-treatment.
투명 세포 난소암 환자의 대표적인 치료 전후 조직검사 결과 치료된 검체의 면역조직 화학적 염색 결과에서 CD8+ T 세포(갈색)의 상당한 증가를 보였습니다.
Source
Kim R, Barve M, Mamdani H, “Initial biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced MSS-colorectal cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
NeoImmuneTech, Phase 1, FIH study
TILs by Immunofluorescence
TILs과 유효성

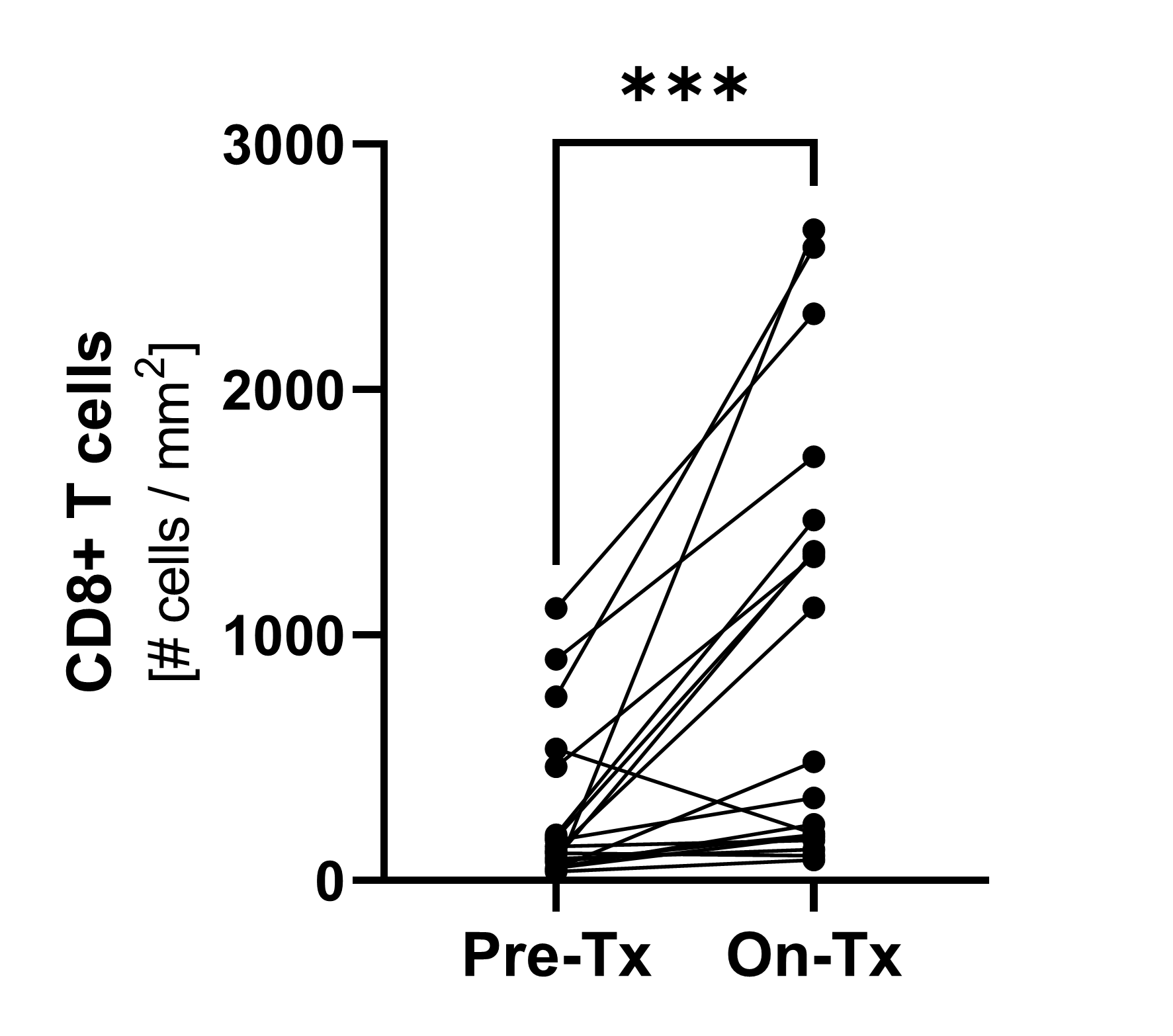
TILs by Immunofluorescence


Pooled data of pre-treatment and on-treatment paired biopsies showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cell infiltration. *p<0.05; ***p<0.0001
TILs과 유효성


Pooled data of pre-treatment and on-treatment paired biopsies showed a significant increase of CD8+ T cell infiltration. *p<0.05; ***p<0.0001
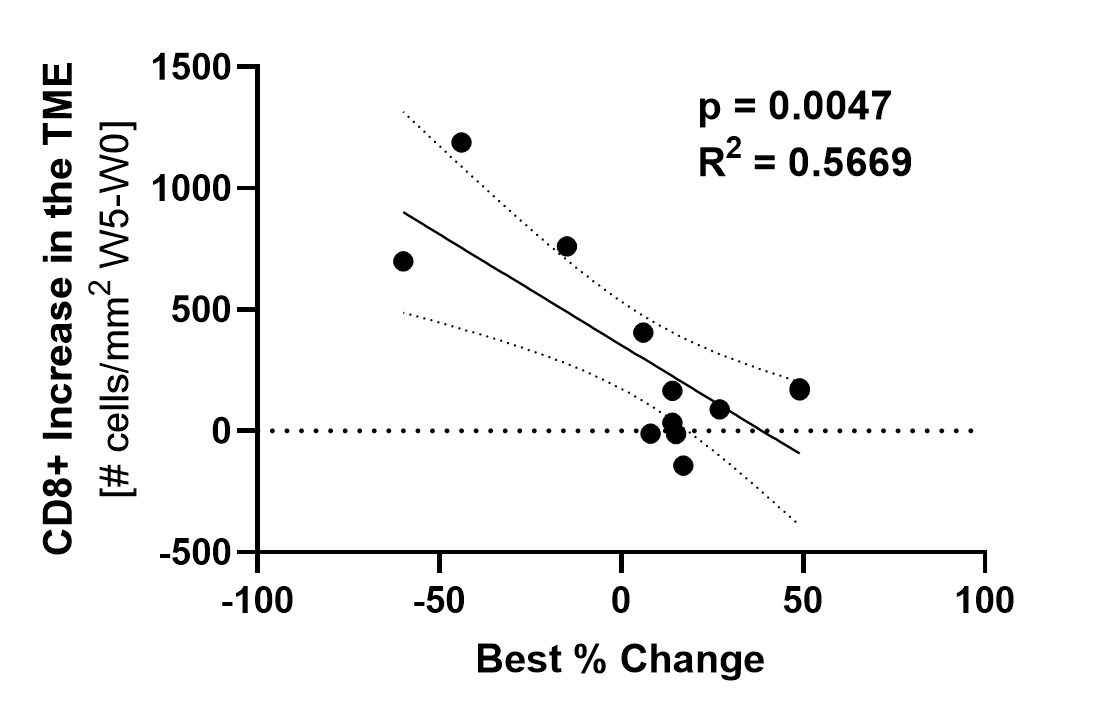
치료에서 TIL(y축)의 높은 증가를 보인 환자는 더 큰 종양 감소(x축)를 보였습니다.
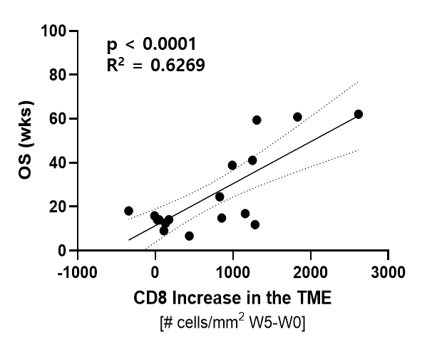
치료에서 TIL(x축)의 높은 증가를 보인 환자는 더 긴 생존율(y축)을 보였습니다.
Wks = 주
Source
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France.
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Ware M, "NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7, plus pembrolizumab favors CD8 T-cell infiltration in liver metastases of heavily pre-treated, immunologically cold, MSS-colorectal and pancreatic cancer" Oral Presentation Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA.
종양 내 림프구(TIL)의 T 세포 수용체(T-Cell Receptor, TCR)의 클론성 증가
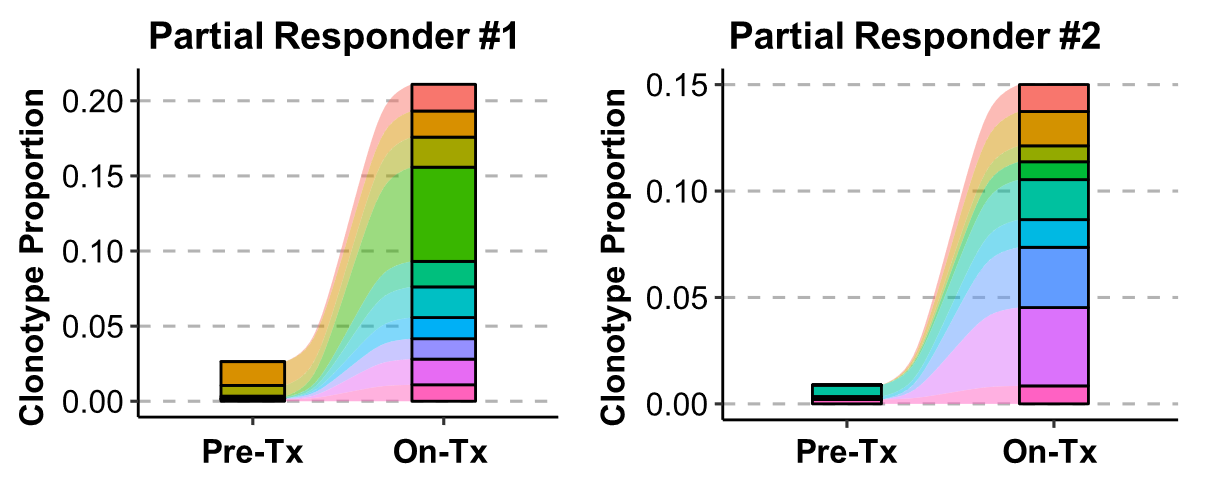
Source
Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France.
줄기세포 특성의 유도
Stem-cell memory CD8+ T cells (Tscm)
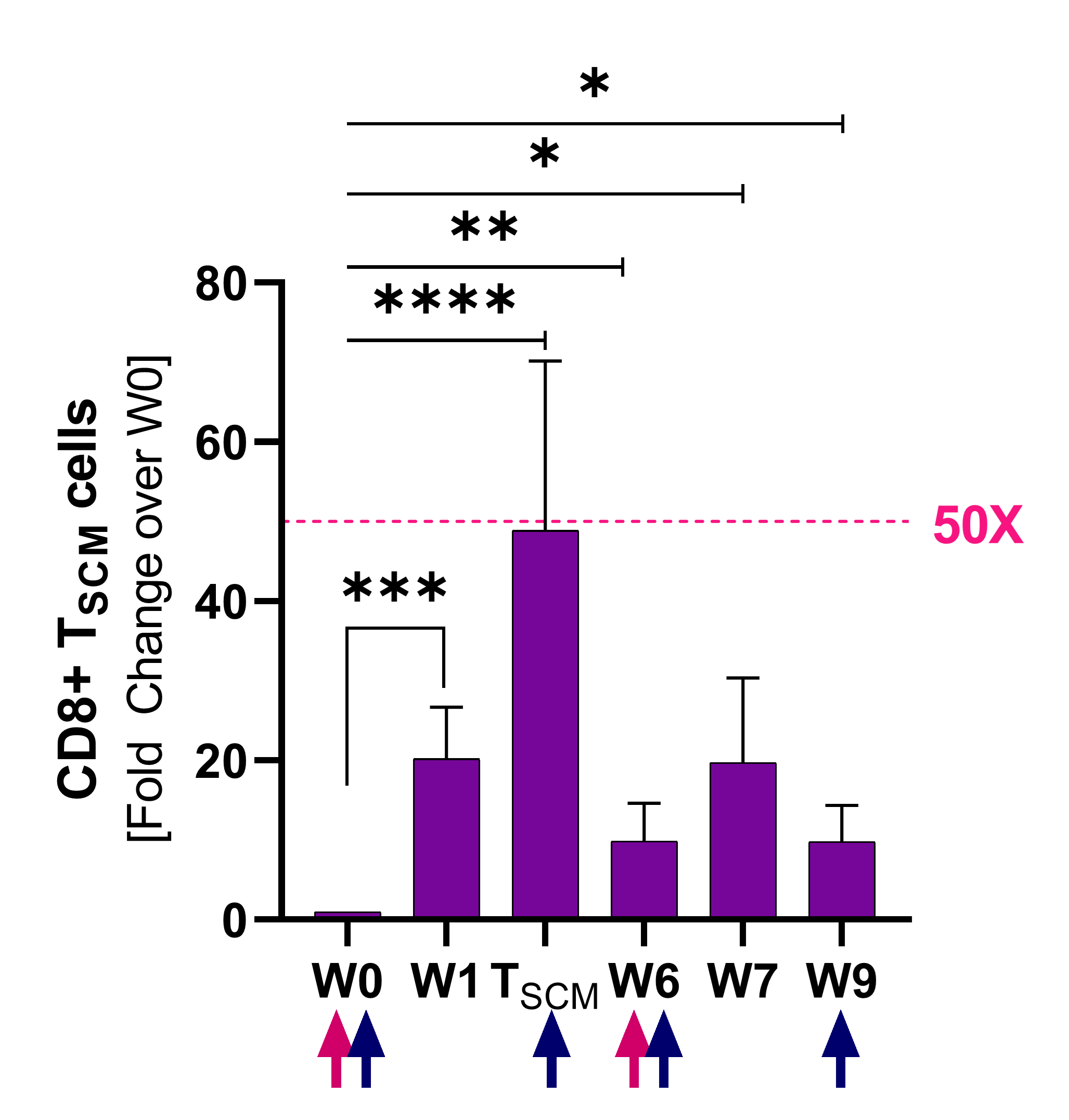
Source
Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C.
연구 포스터 및 논문
NT-I7 임상 연구와 중개 연구 (Clinical studies and translational research) 포스터 및 학회 발표
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Barve M, "NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting IL-7, in combination with pembrolizumab improves T cell fitness in heavily pretreated subjects with gastrointestinal tumors." Poster Presented At SITC; November 1-5, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Lisco A, Ye P, Anderson M, "Cytokine-based immunotherapy with long-acting human recombinant IL-7 in HPV-related diseases associated with idiopathic CD4 lymphopenia." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Perez-Diez A, Liu X, Bennett A, "A long-acting form of recombinant human IL-7 shows biologic effect in both a pre-clinical model and a clinical pilot study of Idiopathic CD4 Lymphopenia." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Webb M, Burns T, Twohy E, "Efficacy and Safety Study of Neoadjuvant Efineptakin alfa (NT-I7) and Pembrolizumab in Recurrent Glioblastoma." Poster Presented At ASCO; June 2-6, 2023; Chicago, IL (Click Here )
- Ghobadi A, Budde L., Galal A, "A Phase 1b Dose Expansion Study Evaluating Safety, Preliminary Anti-Tumor Activity, and Accelerated T Cell Reconstitution with NT-I7 (Efineptakin Alfa), a Long-Acting Human IL-7, Administered Following Tisagenlecleucel in Subjects with Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma." Poster Presented At ASH; Dec 10-13, 2022; New Orleans, LA (Click Here )
- Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Ware M, "NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7, plus pembrolizumab favors CD8 T-cell infiltration in liver metastases of heavily pre-treated, immunologically cold, MSS-colorectal and pancreatic cancer" Oral Presentation Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Butt O, Tao Y, Huang J, "A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 11, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Kang H, Spitzer M, Kim MO, "NT-I7 for the treatment of locally recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck undergoing salvage surgery: a clinical trial in progress" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA (Click Here )
- Naing A, Ferrando-Martinez S, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7 plus pembrolizumab combination treatment enhances infiltration of PD-1+ T cells and provides a more immunogenic tumor microenvironment: Biomarker data from the NIT-110 study" Poster Presented at ESMO; Sep. 1st, 2022; Paris, France. (Click Here )
- Kim R, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced MSS-Colorectal Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jul. 1st, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced Pancreatic Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jun. 30th, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Gastman B, Fling S, Ansstas G, "A phase 1b/2a study of safety and efficacy of NT-I7 in combination with anti-PD-L1 (atezolizumab) in patients with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 naïve or relapsed/refractory (R/R) high-risk skin cancers: The phase 1b report." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 6th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Efficacy and safety of NT-I7, long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: Results from the phase 2a study." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 5th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here ) **Selected for poster discussion session
- Ghobadi A, Budde L, Galal A, "Trial in progress: A phase 1b study evaluating the safety, tolerability, and preliminary anti-tumor activity of NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting human IL-7, post-tisagenlecleucel in subjects with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma" Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 4th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Kim G, Lee K, “Phase 1b/2 study of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent (R/R) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC): The KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 1st, 2022; Chicago, IL.* (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO; Nov 19th, 2021; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Zhou A, Rettig M, Foltz Jennifer. “NT-I7,a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion of CD8 T cells and NK cells and immune activation in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiation” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Kim R, Barve M, Mamdani H, “Initial biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced MSS-colorectal cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy: The interim result of the phase I data.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Fan J, Lee B, “Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics profiles and preliminary antitumor activity of phase 1b/2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: The phase 1b data report.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Im Y, “Efficacy and safety of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab for heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer: The Phase 1b/2 KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at SITC; Oct. 10th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Park K, Ahn H, “Preliminary safety and efficacy of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC): Dose escalation period of Phase Ib/II study (KEYNOTE-899).” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 25th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Lee S, Choi D, Heo M, “Hyleukin-7, a long-acting interleukin-7, increased absolute lymphocyte counts after subcutaneous and intramuscular administration in healthy subjects.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA.* (Click Here )
- Heo M, Sohn J, Lee M, “Phase 1b study of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics profiles in patients with advanced solid cancers.” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 6th, 2019; National Harbor, MD.* (Click Here )
NT-I7 비임상 실험(Nonclinical research) 포스터 및 학회 발표
- Lee SM, Kim M, Ferrando-Martinez S, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin-alfa, NT-I7) increases tumor-specific CD8+ T cells despite FOLFOX cytotoxicity effect." Poster Presented At AACR; April 5-10, 2024; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Xiang J, Devenport J, Carter A, "An “off-the-shelf” CD2 Universal CAR-T therapy combined with a long-acting IL-7 for T-cell malignancies ." Oral Presented At ASH; December 9-12, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Lee M, Ferrando-Martinez S, Im SK, "NT-I7 and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that favors anti-tumor efficacy in combination with checkpoint inhibitors." Poster Presented At SITC; November 1-5, 2023; San Diego, CA (Click Here )
- Li Y, Hu T, Kesarwani A, "Long-acting recombinant interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, improves survival following oncolytic Zika virus treatment in the SB28 immunosuppressive and treatment-resistant murine glioma model." Poster Presented At SNO; November 16-19, 2023; Vancouver, Canada (Click Here )
- Niavi C, Lee J, Valanparambil R, "Effect of NT-I7 treatment on CD4 T cells during chronic LCMV ." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Lee J, Niavi C, Ahn E, "NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion and mobilization of virus-specific PD-1+Tcf-1+ stem-like CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection." Poster Presented At ICIS; October 15-18, 2023; Athens, Greece
- Lee M, Im SK, Baek S, "The combination of NT-I7 and hIL-2/TCB2c promotes the development of an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that enhances the anti-tumor efficacy in combination with checkpoint inhibitors ." Poster Presented At KAI; September 13-16, 2023; Incheon, Korea
- Chen M, Chen I, Supabphol S, "NT-I7 as an adjuvant to DNA neoantigen vaccination enhances and prolongs neoantigen-specific anti-tumor immunity." Poster Presented At AACR; April 14-19, 2023; Orlando, FL (Click Here )
- Phoon Y, Kai K, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a novel long-acting interleukin-7, improves engraftment of patient immune cells and efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in a preclinical humanized melanoma model" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Lee KJ, Tae N, Kang YW, "Redirecting IL-7-induced bystander tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes by bispecific T cell engager augments antitumor response" Poster Presented at SITC; Nov 10, 2022; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Zou Y, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, enhances T cell reconstitution following total body irradiation" Poster Presented at RRS; Oct 17, 2022; Waikoloa Village, HI. (Click Here )
- Zou Y, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, "NT-I7, a long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, enhances T cell reconstitution following total body irradiation" Oral Presentation Presented at RITN; Aug 4, 2022; Alexandria, VA. (Click Here )
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with anti-TIGIT or anti-VEGF" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with hIL-2/TCB2c complex" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Bardahl J, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, “Effects of a novel long-acting IL-7 on T cell reconstitution following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation” Poster Presented at Duke Pediatrics Research Retreat; Apr. 28th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Niavi C, Lee J, McManus D, “Effect of NT-I7 treatment on CD8 T cell differentiation during chronic LCMV” Poster Presented at SIS 2022; Jun. 11th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Liang T, Li, D, Ferrando-Martinez S, “Influence of NT-I7, an engineered long-acting interleukin-7, on CAR T cell therapy in liver cancer” Poster Presented at PEGS 2022; May 4th, 2022, Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. ”A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models.” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Park S, Kim J, Kang Y, “Combination of rhIL-7-hyFc and anti-PD-L1xCD3ε bispecific antibody enhances antitumor response in mice” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 09th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Ghosh S, Yan R, Thotala S, “A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Poster Presented at SITC; Dec. 10th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- O'Neal, Julie, et al. "In vivo efficacy of BCMA-iNKT-CAR is enhanced by NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7.” Oral Presentation Presented at 17th International Myeloma Workshop; Sep. 13th, 2019; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. "Effect of a novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, on survival in mouse models of glioma.” Abstract submitted for ASCO; May. 31st, 2019: e13516. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Hong S, Kim Y, "Hyleukin-7, the Fc-fused interleukin-7, generates anti-tumor activity by modulating both adaptive and innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA. * (Click Here )
- Cooper ML, Staser KW, Niswonge J, "A Long-Acting Pharmacological Grade Interleukin-7 Molecule Logarithmically Accelerates CART Proliferation, Differentiation, and Tumor Killing.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellular Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellule Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Cooper M, Staser K, Davenport J, "A long-acting pharmacological grade interleukin-7 molecule logarithmically accelerates UCAR-T proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing.” Oral Presentation Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Choi D, Ji M, "Preclinical evaluation of the anti-tumor activity of Fc-fused interleukin-7 in both monotherapy and combination therapy.” Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 14th, 2018; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
연구 논문
- Kim, Anhye, et al. "Understanding the pharmacokinetic journey of fc-fusion protein, rhIL-7-hyFc, using complementary approach of two analytical methods, accelerator mass spectrometry and ELISA." Antibody Therapeutics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1093/abt/tbae004
- Kwon, Dong-Il, et al. "Fc-fused IL-7 provides broad antiviral effects against respiratory virus infections through IL-17A-producing pulmonary innate-like T cells." Cell Report Medicine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101362
- Lee, Minji, et al. "rhIL-7-hyFc and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that improves anti-tumor efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors." Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2024). https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2023-008001
- Xiang, Jingyu, et al. "An “off-the-shelf” CD2 Universal CAR-T therapy for T-cell malignancies." Leukemia (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-023-02039-z
- O'Neal, Julie, et al. "Anti-myeloma efficacy of CAR-iNKT is enhanced with a long-acting IL-7, rhIL-7hyFc." Blood Advances (2023). https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010032
- Ware, Michael B. et al. "The Role of Interleukin-7 in the Formation of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Their Prognostic Value in Gastrointestinal Cancers" Journal of Immunotherapy and Precision modalPageOne 5.4 (2022): 105-117. https://doi.org/10.36401/JIPO-22-10
- Kim, Sojeong et al. "A single administration of hIL-7-hyFc induces long-lasting T-cell expansion with maintained functions and TCR diversity" Blood Advances (2022). https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006591
- Kim, Miriam Y. et al. "A long-acting interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, enhances CAR T cell expansion, persistence, and anti-tumor activity" Nature Communications (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30860-0
- Wolfarth, Alexandra A. et al. “Advancements of Common Gamma-Chain Family Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy” Immune Network (2022). https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2022.22.e5
- Campian, Jian L. et al. “Long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 + T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Clinical Cancer Research (2022). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0947
- Kim, Miriam Y, et al. “CD7-deleted hematopoietic stem cells can restore immunity after CAR T cell therapy” JCI Insight (2021). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.149819
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Cancer immunotherapy with T-cell targeting cytokines: IL-2 and IL-7.” BMB Reports (2021). https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.1.257
- Foluso O Ademuyiwa, et al. “Immunogenomic profiling and pathological response results from a clinical trial of docetaxel and carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer.” Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06307-3
- Kim, Sora, et al. “Fc-fused IL-7 mobilizes long-term HSCs in a pro-B cell-dependent manner and synergizes with G-CSF and AMD3100.” Leukemia(2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01274-6
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Hybrid Fc-fused interleukin-7 induces an inflamed tumor microenvironment and improves the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.” Clinical and Translational Immunology (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cti2.1168
- Lee, Sang Won, et al. "hIL-7-hyFc, a long-acting IL-7, increased absolute lymphocyte count in healthy subjects.” Clinical and Translational Science (2020). [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12800
- Choi, Young Woo, et al. "Intravaginal administration of Fc-fused IL7 suppresses the cervicovaginal tumor by recruiting HPV DNA vaccine-induced CD8 T cells." Clinical Cancer Research 22.23 (2016): 5898-5908. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0423
- Lim, Jun Yeul, et al. "Biophysical stability of hyFc fusion protein with regards to buffers and various excipients." International journal of biological macromolecules 86 (2016): 622-629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.006
- Kang, Moon Cheol, et al. "Intranasal introduction of Fc-fused interleukin-7 provides long-lasting prophylaxis against lethal influenza virus infection." Journal of virology 90.5 (2016): 2273-2284. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02768-15
- Seo, Yong Bok, et al. "Crucial roles of interleukin-7 in the development of T follicular helper cells and in the induction of humoral immunity." Journal of virology 88.16 (2014): 8998-9009. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00534-14
- Ahn, So-Shin, et al. "Nonlytic Fc-fused NT-I7 synergizes with Mtb32 DNA vaccine to enhance antigen-specific T cell responses in a therapeutic model of tuberculosis." Vaccine 31.27 (2013): 2884-2890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.029
- Nam, Hyo Jung, et al. "Marked enhancement of antigen‐specific T‐cell responses by IL‐7‐fused nonlytic, but not lytic, Fc as a genetic adjuvant." European journal of immunology 40.2 (2010): 351-358. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939271
NT-I7의 면역질환 치료 관여 기작
T세포는 외부 병균체의 공격을 방어하기 위한 면역 시스템 형성에 필수적인 역할을 합니다.
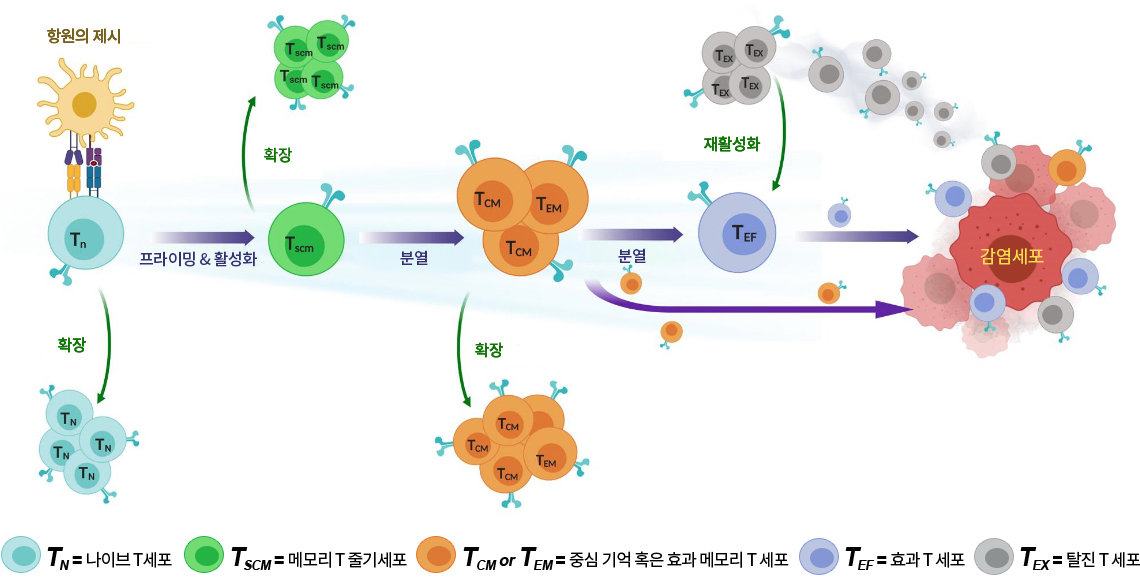
1. 항상성의 유지
- 가슴샘 림프구 (Thymopoiesis) 증식
- 나이브 T 세포숫자의 증가
- 메모리 T줄기세포를 포함한 다양한 체내 휴면 T세포의 안정적인 확보
2. 최초 면역 반응
- 나이브 T세포의 숫자를 증가시키고 T세포 수용체의 다양성을 넓힘
- 약한 항원에 대한 민감성을 높힘
- T세포 수용체 (TCR) 신호기작과 상승 작용을 함
3. 적응면역계 반응
- 메모리 T세포 분화와 회전을 촉진
- T세포 탈진을 제한
- 만성적 항원의 자극에도 지속적인 면역 반응을 유지
네오이뮨텍은 면역 저항력이 약한 계층을 대상으로 NT-I7의 면역 재구성과 향상에 관한 잠재적 효과를 알아보기 위한 임상 시험을 진행하고 있습니다.
- 임상시험 번호 (NCT04054752)에서는 NT-I7의 안전성과 면역기능 재구성 및 백신에 대한 반응을 항암 약물요법 (Chemotherapy)을 받았던 노인계층
암 생존자를 대상으로 연구하고 있습니다. - NT-I7은 원인이 알려져 있지 않은 CD4+ 림프구 감소증 (Idiopathic CD4+ Lymphocytopenia, ICL)의 치료용도로 희귀의약품 지정을 유럽의약청 (EMA)에서는 2017년에, 미 식품 의약청 FDA 에서는 2019년에 받았습니다. 네오이뮨텍 (NIT)는 미 과학부 (NIH) 연구자들과 ICL환자들에게 있을 수 있는 NT-I7의 잠재적 치료 효과를 알아보기 위해 임상 연구를 디자인 하고 있습니다.
연구 포스터 및 논문
NT-I7 임상 연구 (Clinical Research) 포스터 및 학회 발표
- Kim R, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced MSS-Colorectal Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jul. 1st, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Phase 2a Study of NT-I7, a Long-Acting Interleukin-7, plus Pembrolizumab: Cohort of Subjects with Checkpoint Inhibitor-Naïve Advanced Pancreatic Cancer" Poster Presented at ESMO-GI; Jun. 30th, 2022; Barcelona, Spain. (Click Here )
- Gastman B, Fling S, Ansstas G, "A phase 1b/2a study of safety and efficacy of NT-I7 in combination with anti-PD-L1 (atezolizumab) in patients with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 naïve or relapsed/refractory (R/R) high-risk skin cancers: The phase 1b report." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 6th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Mamdani H, Brave M, "Efficacy and safety of NT-I7, long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: Results from the phase 2a study." Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 5th, 2022; Chicago, IL. (Click Here ) **Selected for poster discussion session
- Ghobadi A, Budde L, Galal A, "Trial in progress: A phase 1b study evaluating the safety, tolerability, and preliminary anti-tumor activity of NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting human IL-7, post-tisagenlecleucel in subjects with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma" Poster Presented (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Kim G, Lee K, “Phase 1b/2 study of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent (R/R) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC): The KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at ASCO; Jun. 1st, 2022; Chicago, IL.* (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study evaluating the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO; Nov 19th, 2021; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Zhou A, Rettig M, Foltz Jennifer. “NT-I7,a long-acting interleukin-7, promotes expansion of CD8 T cells and NK cells and immune activation in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiation” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Kim R, Barve M. “Preliminary biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced pancreatic cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Kim R, Barve M, Mamdani H, “Initial biomarker and clinical data of a phase 2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab: cohort of subjects with checkpoint inhibitor-naïve advanced MSS-colorectal cancer” Poster Presented at SITC; Sep. 13th, 2021; Washington, D.C. (Click Here )
- Campian Jian Li, et al. “A phase I/II study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a novel long-acting interleukin-7, NT-I7, for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas after chemoradiotherapy: The interim result of the phase I data.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Naing A, Fan J, Lee B, “Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics profiles and preliminary antitumor activity of phase 1b/2a study of NT-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: The phase 1b data report.” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 28th, 2021; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Im Y, “Efficacy and safety of GX-I7 plus pembrolizumab for heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer: The Phase 1b/2 KEYNOTE-899 Study.” Poster Presented at SITC; Oct. 10th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Sohn J, Park K, Ahn H, “Preliminary safety and efficacy of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with refractory or recurrent metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC): Dose escalation period of Phase Ib/II study (KEYNOTE-899).” Poster Presented at ASCO; May. 25th, 2020; Virtual Presentation.* (Click Here )
- Lee S, Choi D, Heo M, “Hyleukin-7, a long-acting interleukin-7, increased absolute lymphocyte counts after subcutaneous and intramuscular administration in healthy subjects.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA.* (Click Here )
- Heo M, Sohn J, Lee M, “Phase 1b study of GX-I7, a long-acting interleukin-7, evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics profiles in patients with advanced solid cancers.” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 6th, 2019; National Harbor, MD.* (Click Here )
NT-I7 전 임상 실험과 중개 연구 (Preclinical and Translational Research) 포스터 및 학회 발표
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with anti-TIGIT or anti-VEGF" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Baek S, Im SK, Lee M, "rhIL-7-hyFc (efineptakin alpha; NT-I7) enhances the anti-tumor response when combined with hIL-2/TCB2c complex" Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 13th, 2022; New Orleans, LA. (Click Here )
- Bardahl J, Jiao Y, Wolfarth A, “Effects of a novel long-acting IL-7 on T cell reconstitution following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation” Poster Presented at Duke Pediatrics Research Retreat; Apr. 28th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Niavi C, Lee J, McManus D, “Effect of NT-I7 treatment on CD8 T cell differentiation during chronic LCMV” Poster Presented at SIS 2022; Jun. 11th, 2022; Durham, NC. (Click Here )
- Liang T, Li, D, Ferrando-Martinez S, “Influence of NT-I7, an engineered long-acting interleukin-7, on CAR T cell therapy in liver cancer” Poster Presented at PEGS 2022; May 4th, 2022, Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. ”A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models.” Oral Presentation Presented at SNO 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Park S, Kim J, Kang Y, “Combination of rhIL-7-hyFc and anti-PD-L1xCD3ε bispecific antibody enhances antitumor response in mice” Poster Presented at SITC; Nov. 09th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- Ghosh S, Yan R, Thotala S, “A novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Poster Presented at SITC; Dec. 10th 2020; Virtual Presentation. (Click Here )
- O'Neal, Julie, et al. "In vivo efficacy of BCMA-iNKT-CAR is enhanced by NT-I7, a long-acting IL-7.” Oral Presentation Presented at 17th International Myeloma Workshop; Sep. 13th, 2019; Boston, MA. (Click Here )
- Campian, Jian Li, et al. "Effect of a novel long-acting interleukin-7 agonist, NT-I7, on survival in mouse models of glioma.” Abstract submitted for ASCO; May. 31st, 2019: e13516. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Hong S, Kim Y, "Hyleukin-7, the Fc-fused interleukin-7, generates anti-tumor activity by modulating both adaptive and innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.” Poster Presented at AACR; Mar. 30th, 2019; Atlanta, GA. * (Click Here )
- Cooper ML, Staser KW, Niswonge J, "A Long-Acting Pharmacological Grade Interleukin-7 Molecule Logarithmically Accelerates CART Proliferation, Differentiation, and Tumor Killing.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellular Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at TCT-Transplant & Cellule Therapy: Feb. 20th, 2019; Houston, TX. (Click Here )
- Staser KW, Cooper ML, Choi J, "Modeling Sezary Syndrome For Immunophenotyping and Anti-Tumor Effect of Ucart and Long-Acting Interleukin-7 Combination Therapy.” Poster Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Cooper M, Staser K, Davenport J, "A long-acting pharmacological grade interleukin-7 molecule logarithmically accelerates UCAR-T proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing.” Oral Presentation Presented at ASH Annual Meeting; Dec. 2nd, 2018; San Diego, CA. (Click Here )
- Kim J, Choi D, Ji M, "Preclinical evaluation of the anti-tumor activity of Fc-fused interleukin-7 in both monotherapy and combination therapy.” Poster Presented at AACR; Apr. 14th, 2018; Chicago, IL. (Click Here )
연구 논문
- Kim, Miriam Y. et al. "A long-acting interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, enhances CAR T cell expansion, persistence, and anti-tumor activity" Nature Communications (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30860-0
- Wolfarth, Alexandra A. et al. “Advancements of Common Gamma-Chain Family Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy” Immune Network (2022). https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2022.22.e5
- Campian, Jian L. et al. “Long-acting recombinant human interleukin-7, NT-I7, increases cytotoxic CD8 + T cells and enhances survival in mouse glioma models” Clinical Cancer Research (2022). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0947
- Kim, Miriam Y, et al. “CD7-deleted hematopoietic stem cells can restore immunity after CAR T cell therapy” JCI Insight (2021). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.149819
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Cancer immunotherapy with T-cell targeting cytokines: IL-2 and IL-7.” BMB Reports (2021). https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.1.257
- Foluso O Ademuyiwa, et al. “Immunogenomic profiling and pathological response results from a clinical trial of docetaxel and carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer.” Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06307-3
- Kim, Sora, et al. “Fc-fused IL-7 mobilizes long-term HSCs in a pro-B cell-dependent manner and synergizes with G-CSF and AMD3100.” Leukemia(2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01274-6
- Kim, Ji-Hae, et al. “Hybrid Fc-fused interleukin-7 induces an inflamed tumor microenvironment and improves the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.” Clinical and Translational Immunology (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cti2.1168
- Lee, Sang Won, et al. "hIL-7-hyFc, a long-acting IL-7, increased absolute lymphocyte count in healthy subjects.” Clinical and Translational Science (2020). [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12800
- Choi, Young Woo, et al. "Intravaginal administration of Fc-fused IL7 suppresses the cervicovaginal tumor by recruiting HPV DNA vaccine-induced CD8 T cells." Clinical Cancer Research 22.23 (2016): 5898-5908. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0423
- Lim, Jun Yeul, et al. "Biophysical stability of hyFc fusion protein with regards to buffers and various excipients." International journal of biological macromolecules 86 (2016): 622-629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.006
- Kang, Moon Cheol, et al. "Intranasal introduction of Fc-fused interleukin-7 provides long-lasting prophylaxis against lethal influenza virus infection." Journal of virology 90.5 (2016): 2273-2284. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02768-15
- Seo, Yong Bok, et al. "Crucial roles of interleukin-7 in the development of T follicular helper cells and in the induction of humoral immunity." Journal of virology 88.16 (2014): 8998-9009. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00534-14
- Ahn, So-Shin, et al. "Nonlytic Fc-fused NT-I7 synergizes with Mtb32 DNA vaccine to enhance antigen-specific T cell responses in a therapeutic model of tuberculosis." Vaccine 31.27 (2013): 2884-2890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.029
- Nam, Hyo Jung, et al. "Marked enhancement of antigen‐specific T‐cell responses by IL‐7‐fused nonlytic, but not lytic, Fc as a genetic adjuvant." European journal of immunology 40.2 (2010): 351-358. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939271